Reference: P. Winston, 1992.
Factors Affecting Sunburn
Given Data
| Independent Attributes / Condition Attributes | Dependent Attributes / Decision Attributes | ||||
| Name | Hair | Height | Weight | Lotion | Result |
| Sarah | blonde | average | light | no | sunburned (positive) |
| Dana | blonde | tall | average | yes | none (negative) |
| Alex | brown | short | average | yes | none |
| Annie | blonde | short | average | no | sunburned |
| Emily | red | average | heavy | no | sunburned |
| Pete | brown | tall | heavy | no | none |
| John | brown | average | heavy | no | none |
| Katie | blonde | short | light | yes | none |
Phase 1: From Data to Tree
Perform average entropy calculations on the complete data set for each of the four attributes:
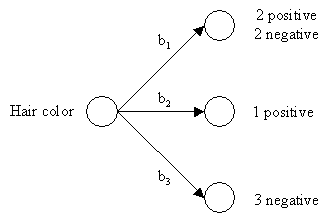
b1 = blonde
b2 = red
b3 = brownAverage Entropy = 0.50
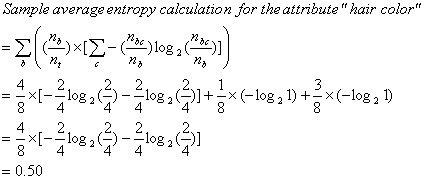
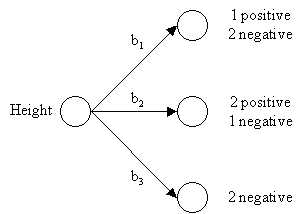
b1 = short
b2 = average
b3 = tallAverage Entropy = 0.69
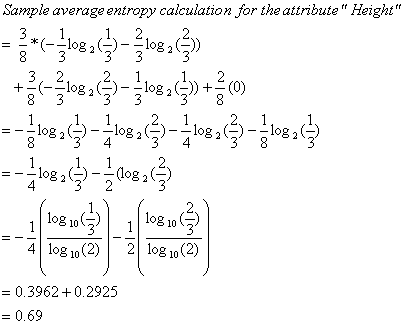
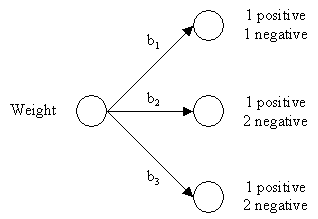
b1 = light
b2 = average
b3 = heavyAverage Entropy = 0.94
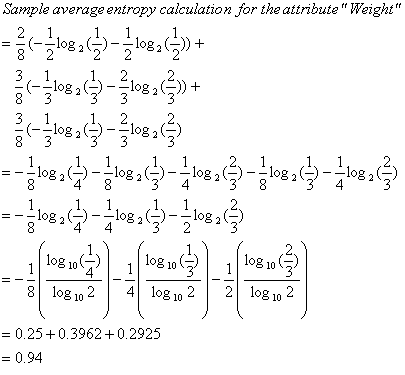
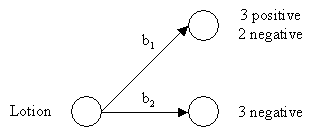
b1 = no
b2 = yes
Average Entropy = 0.61

Results
Attribute Average Entropy Hair Color 0.50 Height 0.69 Weight 0.94 Lotion 0.61 The attribute "hair color" is selected as the first test because it minimizes the entropy.
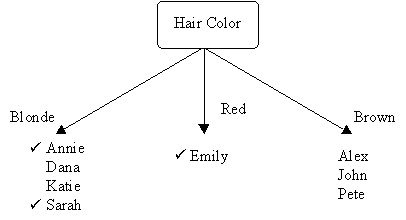
- Similarily, we now choose another test to separate out the sunburned individuals from the blonde haired inhomogeneous subset, {Sarah, Dana, Annie, and Katie}.
Results
Attribute Average Entropy Height 0.50 Weight 1.00 Lotion 0.00 The attribute "lotion" is selected because it minimizes the entropy in the blonde hair subset.
Thus, using the "hair color" and "lotion" tests together ensures the proper identification of all the samples.
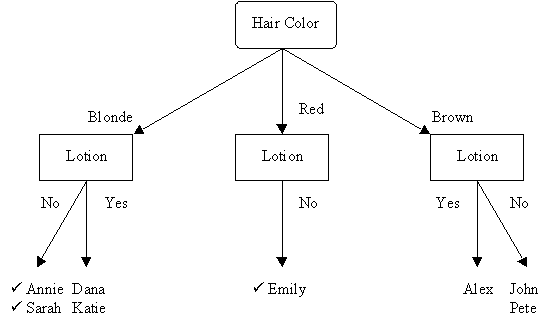
This is the completed decision tree.


