Reference: E. Rich, K. Knight, "Artificial Intelligence", McGraw Hill, Second Edition.
http://www.cc.gatech.edu/classes/cs3361_97_winter/learning.txt
Problem 1:
Learning the concept of "Japanese Economy Car"
Features: ( Country of Origin, Manufacturer, Color, Decade, Type )
| Origin | Manufacturer | Color | Decade | Type | Example Type |
| Japan | Honda | Blue | 1980 | Economy | Positive |
| Japan | Toyota | Green | 1970 | Sports | Negative |
| Japan | Toyota | Blue | 1990 | Economy | Positive |
| USA | Chrysler | Red | 1980 | Economy | Negative |
| Japan | Honda | White | 1980 | Economy | Positive |
Solution:
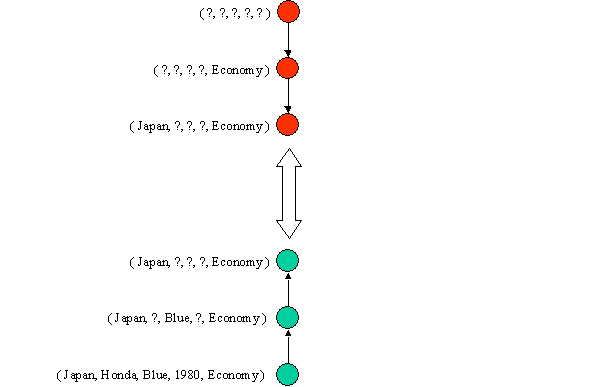
1. Positive Example: (Japan, Honda, Blue, 1980, Economy)
| Initialize G to a singleton set that includes everything. Initialize S to a singleton set that includes the first positive example. |
G = { (?, ?, ?, ?, ?) } S = { (Japan, Honda, Blue, 1980, Economy) } |


These models represent the most general and the most specific heuristics one might learn.
The actual heuristic to be learned, "Japanese Economy Car", probably lies between them somewhere within the version space.
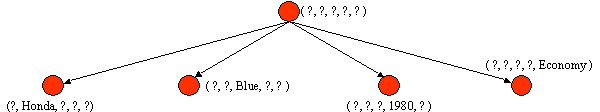
2. Negative Example: (Japan, Toyota, Green, 1970, Sports)
Specialize G to exclude the negative example.
| G = | { (?, Honda, ?, ?, ?), (?, ?, Blue, ?, ?), (?, ?, ?, 1980, ?), (?, ?, ?, ?, Economy) } |
| S = | { (Japan, Honda, Blue, 1980, Economy) } |

Refinement occurs by generalizing S or specializing G, until the heuristic hopefully converges to one that works well.
3. Positive Example: (Japan, Toyota, Blue, 1990, Economy)
Prune G to exclude descriptions inconsistent with the positive example. 
Generalize S to include the positive example.
| G = | { (?, ?, Blue, ?, ?), (?, ?, ?, ?, Economy) } |
| S = | { (Japan, ?, Blue, ?, Economy) } |
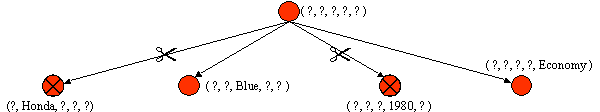

4. Negative Example: (USA, Chrysler, Red, 1980, Economy)
Specialize G to exclude the negative example (but stay consistent with S)
| G = | { (?, ?, Blue, ?, ?), (Japan, ?, ?, ?, Economy) } |
| S = | { (Japan, ?, Blue, ?, Economy) } |
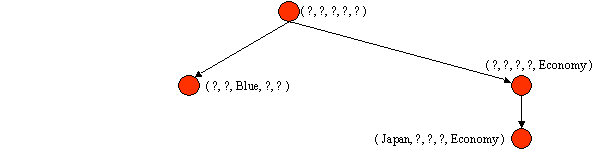

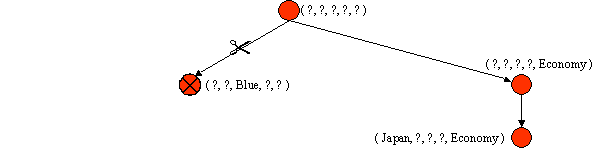
5. Positive Example: (Japan, Honda, White, 1980, Economy)
Prune G to exclude descriptions inconsistent with positive example.
Generalize S to include positive example.
S = { (Japan, ?, ?, ?, Economy) }
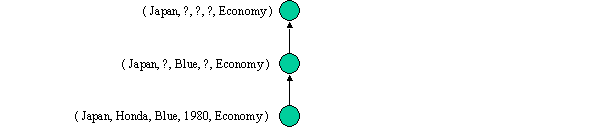
G and S are singleton sets and S = G.
Converged.
No more data, so algorithm stops.